Oregano vs. Parsley — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Oregano contains significantly more vitamins and minerals than parsley.
In recent years, parsley and oregano have been at the center of scientific attention. While parsley is more researched, both are excellent sources of antioxidants and vitamins in the daily diet.
Introduction
Herbs and spices are a perfect way to add a range of flavors to any dish. Both parsley and oregano are ideal herbs and spices.
Parsley belongs to the Umbelliferae family, also known as the carrot or celery family. On the other hand, oregano is botanically classified in the family of mints. Oregano owes its flavor to compounds such as thymol, carvacrol, ocimene, pinene, limonene, and caryophyllene.
In this article, we are going to compare parsley and oregano, focusing on their nutritional differences and health impacts.
Nutritional Content
Parsley is richer in vitamins C, K, and A. On the other hand, oregano contains higher amounts of vitamins E, B complex (B1, B2, B3, B5, and B6), and folate.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+2334.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+105.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+438.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+253.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+130.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+1060%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+55.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+5682.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+395.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+163.8%
When comparing their mineral profile, oregano is richer in phosphorus, iron, calcium, zinc, copper, magnesium, and potassium.
While both of these plants are low in sodium, oregano contains less.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+440%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+1057.2%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+127.4%
Contains
more
IronIron
+493.5%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+324.8%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+151.4%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+155.2%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-55.4%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+3018.8%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+4400%
Health Impact
Myricetin, a flavonoid found in parsley, helps prevent skin cancer (1).
Parsley can also decrease the risk of developing type 2 diabetes (2).
One study has shown the antiviral potential of oregano against norovirus infections (3).
Generally, parsley and oregano have protective roles against the following:
- Cancer prevention (1, 4)
- Antibacterial properties (5, 6)
- Anti-inflammatory properties (7, 8)
- Bone health improvement
Parsley has antiosteoporotic effects on bone tissue (9).
Cardiovascular health
Parsley has negative inotropic and chronotropic properties, leading to hypotensive activity. Additionally, it has a strong antiplatelet aggregation effect. These effects are crucial in reducing cardiovascular risk (10).
Oregano may also lower blood pressure by increasing endothelial NO, an important vasodilator, and binding PPARγ. This effect is distinct from parsley's mechanisms (11).
Furthermore, both parsley and oregano have a diuretic effect, which can be beneficial for managing hypertension and heart failure (12, 13).
It should be noted that oregano oil (at doses of 100 and 200 mg/kg) reduced the incidence of cardiac complications in rats with doxorubicin-induced myocardial infarction (14).
According to this study, oregano's anti-inflammatory properties may help prevent atherosclerosis. Further research is needed to confirm these findings (15).
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5629766/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16223573/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24779581/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6680447/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27525894/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6152729/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5322505/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5801825/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4891838/
- https://cloudfront.net/87763441/6-IJCBS
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jf802298w
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11849841/
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11094-023-02795-3
- https://phcog.com/article/view/2018/14/57s/s363-s368
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0278691510001754
Infographic
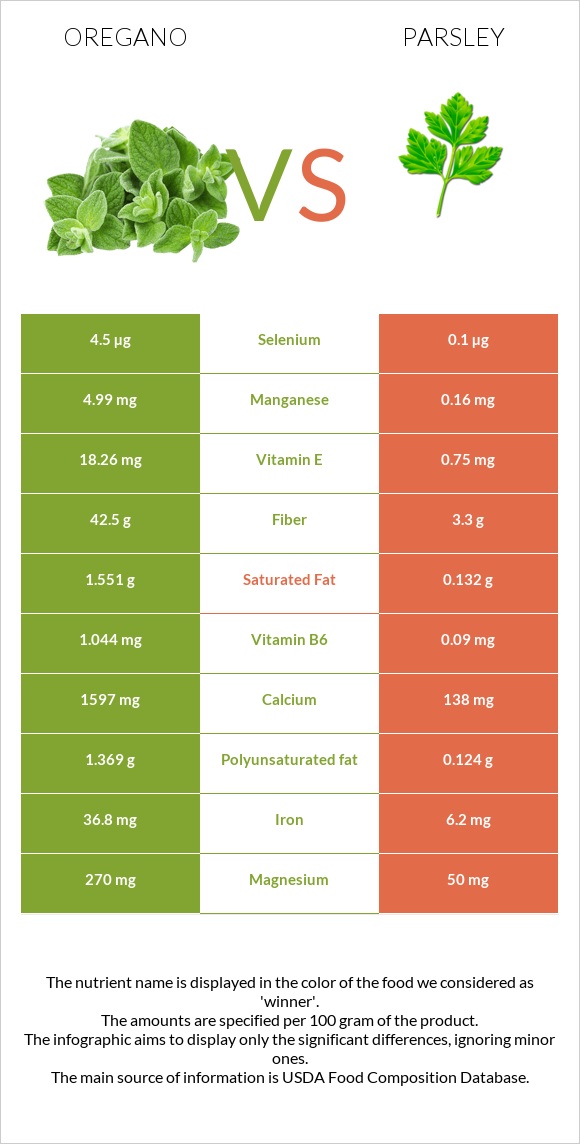
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin K | 621.7µg | 1640µg | 849% |
| Iron | 36.8mg | 6.2mg | 383% |
| Manganese | 4.99mg | 0.16mg | 210% |
| Fiber | 42.5g | 3.3g | 157% |
| Calcium | 1597mg | 138mg | 146% |
| Vitamin C | 2.3mg | 133mg | 145% |
| Vitamin E | 18.26mg | 0.75mg | 117% |
| Vitamin B6 | 1.044mg | 0.09mg | 73% |
| Copper | 0.633mg | 0.149mg | 54% |
| Magnesium | 270mg | 50mg | 52% |
| Vitamin A | 85µg | 421µg | 37% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.528mg | 0.098mg | 33% |
| Carbs | 68.92g | 6.33g | 21% |
| Potassium | 1260mg | 554mg | 21% |
| Vitamin B3 | 4.64mg | 1.313mg | 21% |
| Folate | 237µg | 152µg | 21% |
| Zinc | 2.69mg | 1.07mg | 15% |
| Phosphorus | 148mg | 58mg | 13% |
| Protein | 9g | 2.97g | 12% |
| Calories | 265kcal | 36kcal | 11% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.921mg | 0.4mg | 10% |
| Selenium | 4.5µg | 0.1µg | 8% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.177mg | 0.086mg | 8% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.369g | 0.124g | 8% |
| Saturated fat | 1.551g | 0.132g | 6% |
| Fats | 4.28g | 0.79g | 5% |
| Choline | 32.3mg | 12.8mg | 4% |
| Sodium | 25mg | 56mg | 1% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.716g | 0.295g | 1% |
| Fructose | 1.13g | 1% | |
| Net carbs | 26.42g | 3.03g | N/A |
| Sugar | 4.09g | 0.85g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.203mg | 0.045mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.322mg | 0.122mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.441mg | 0.118mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.78mg | 0.204mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.5mg | 0.181mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.127mg | 0.042mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.449mg | 0.145mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.585mg | 0.172mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.144mg | 0.061mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.621g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +203% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +441.8% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +988.8% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +257.7% |
| Contains more WaterWater | +783.3% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +142.7% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +1004% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -91.5% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Oregano - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171328/nutrients
- Parsley - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170416/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





